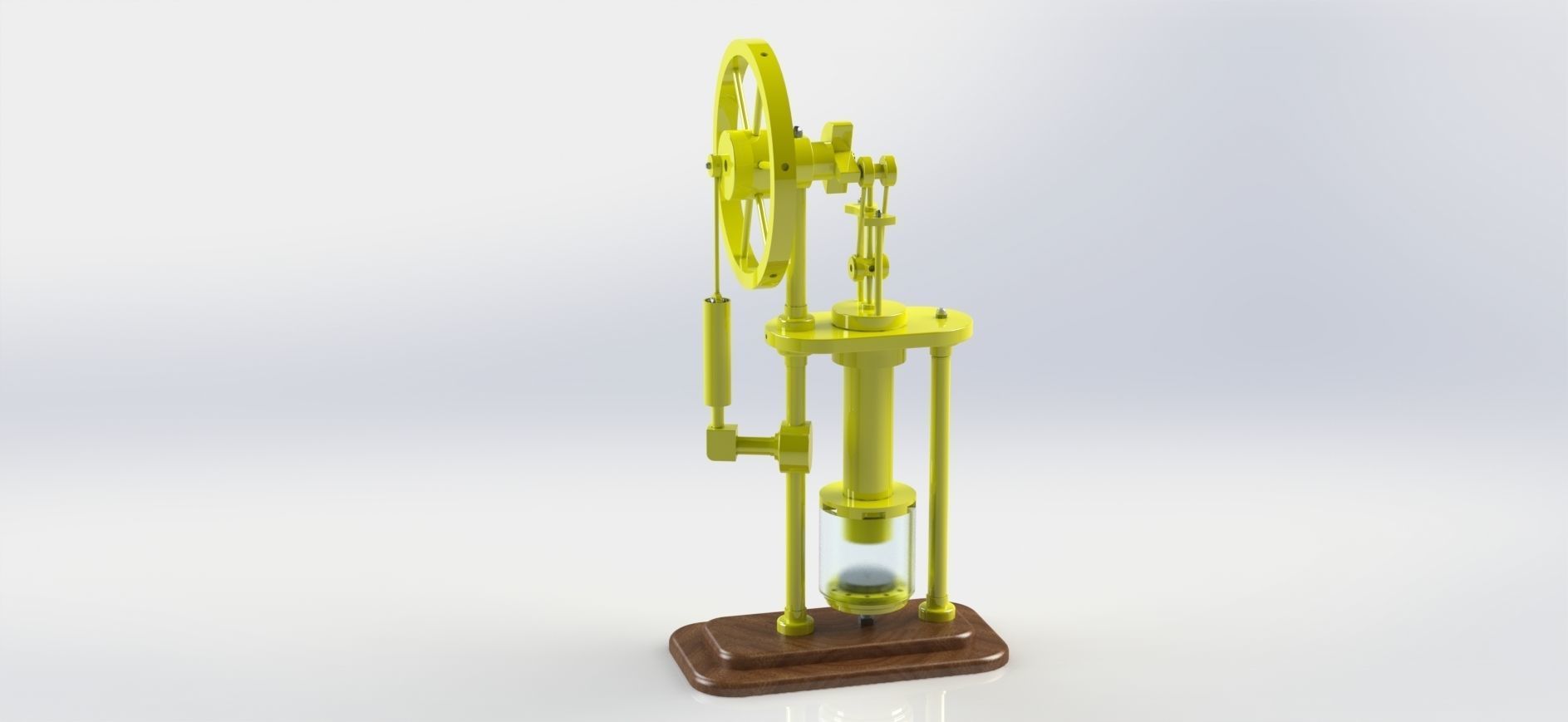
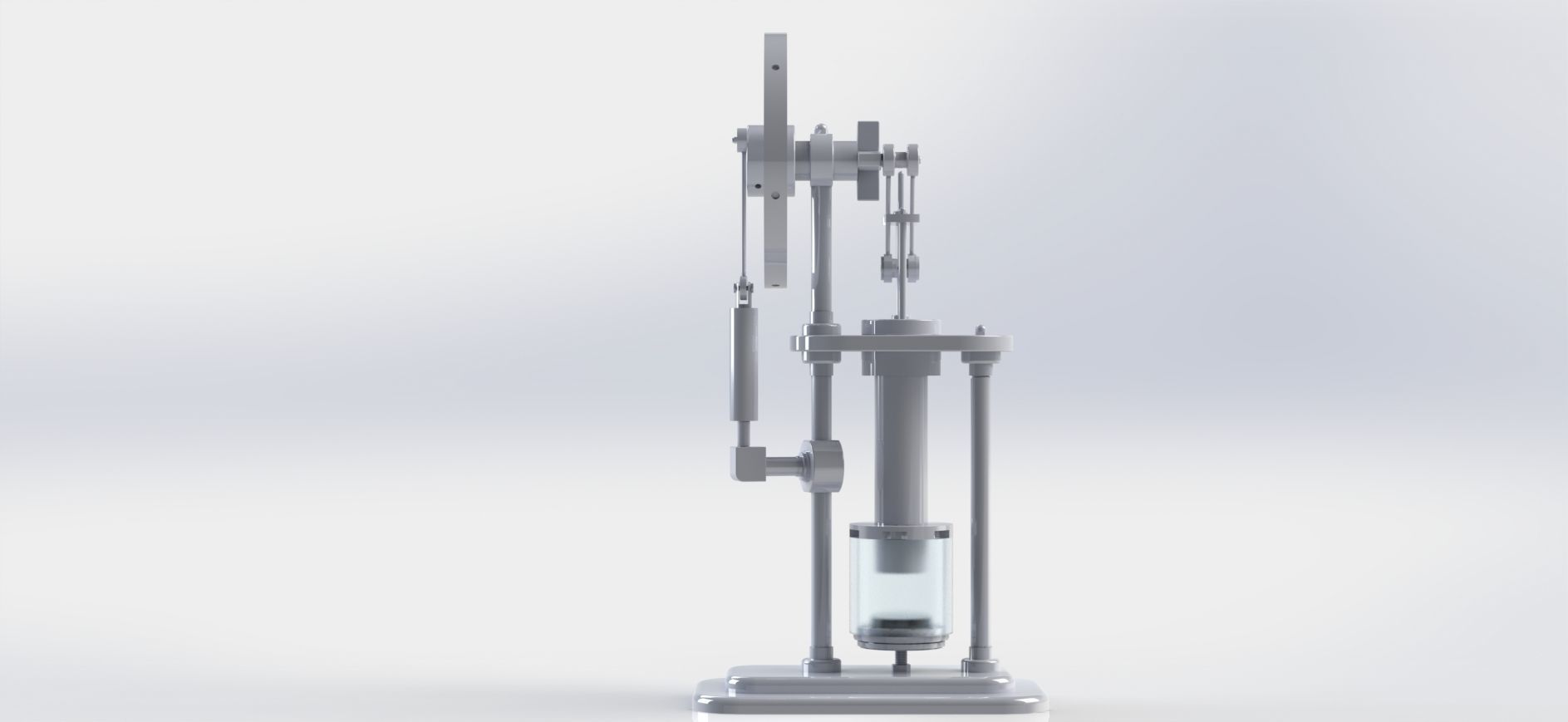
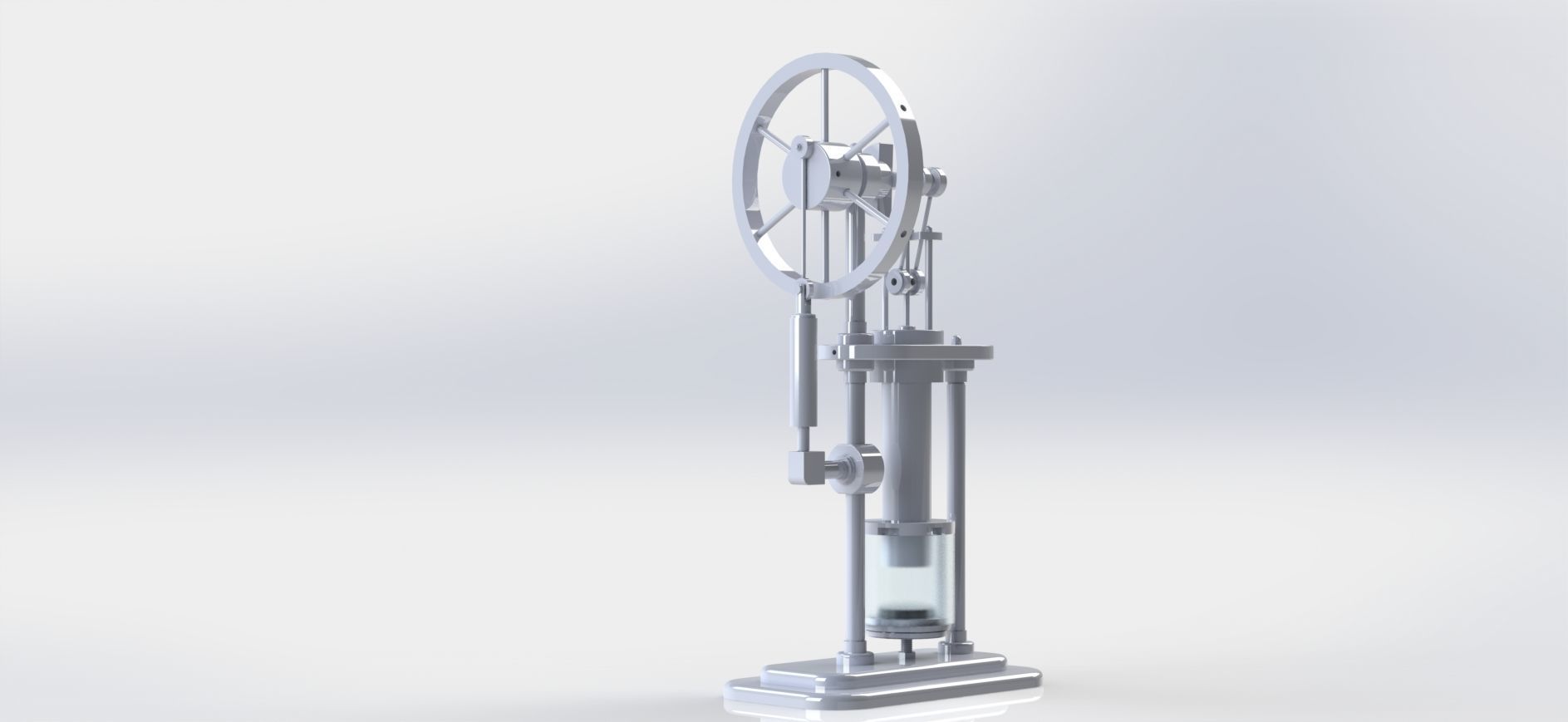
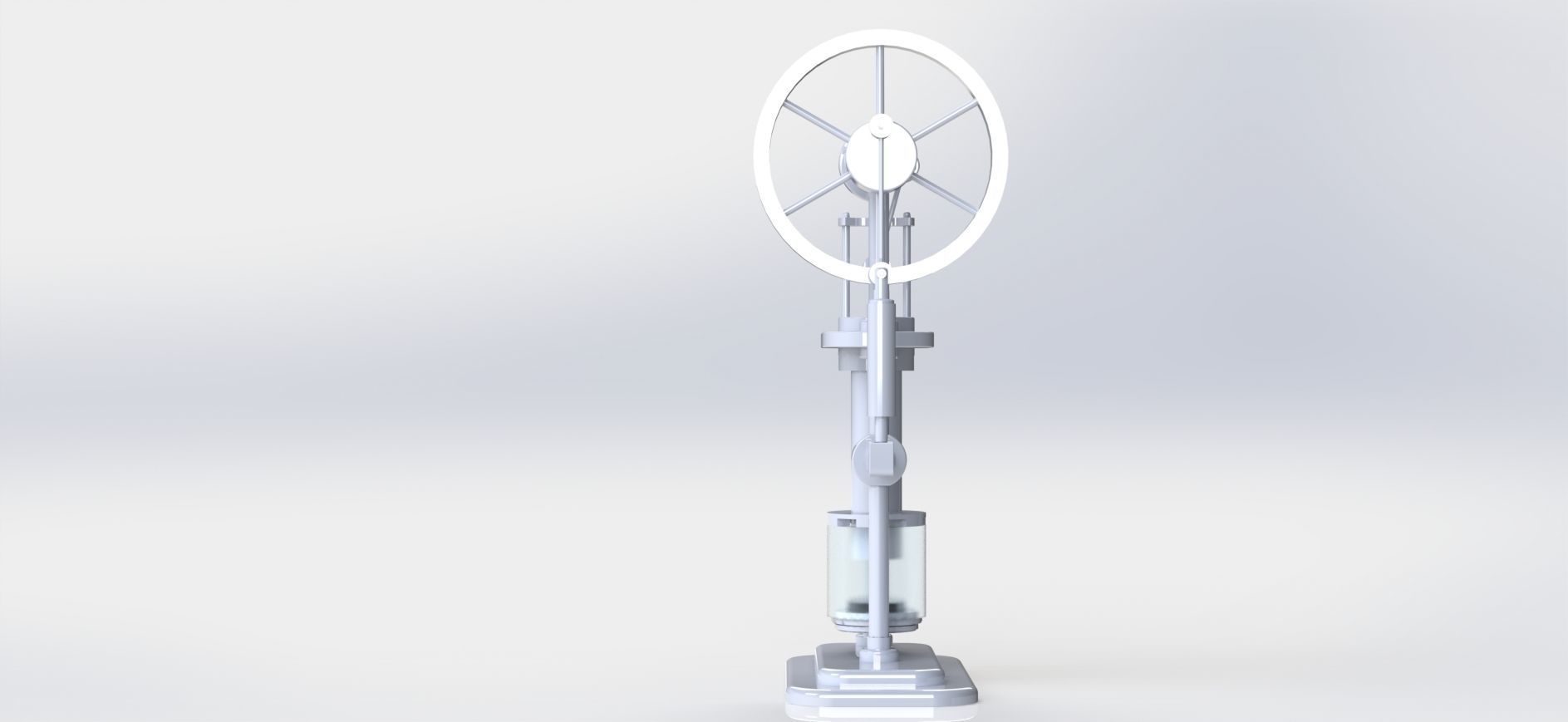
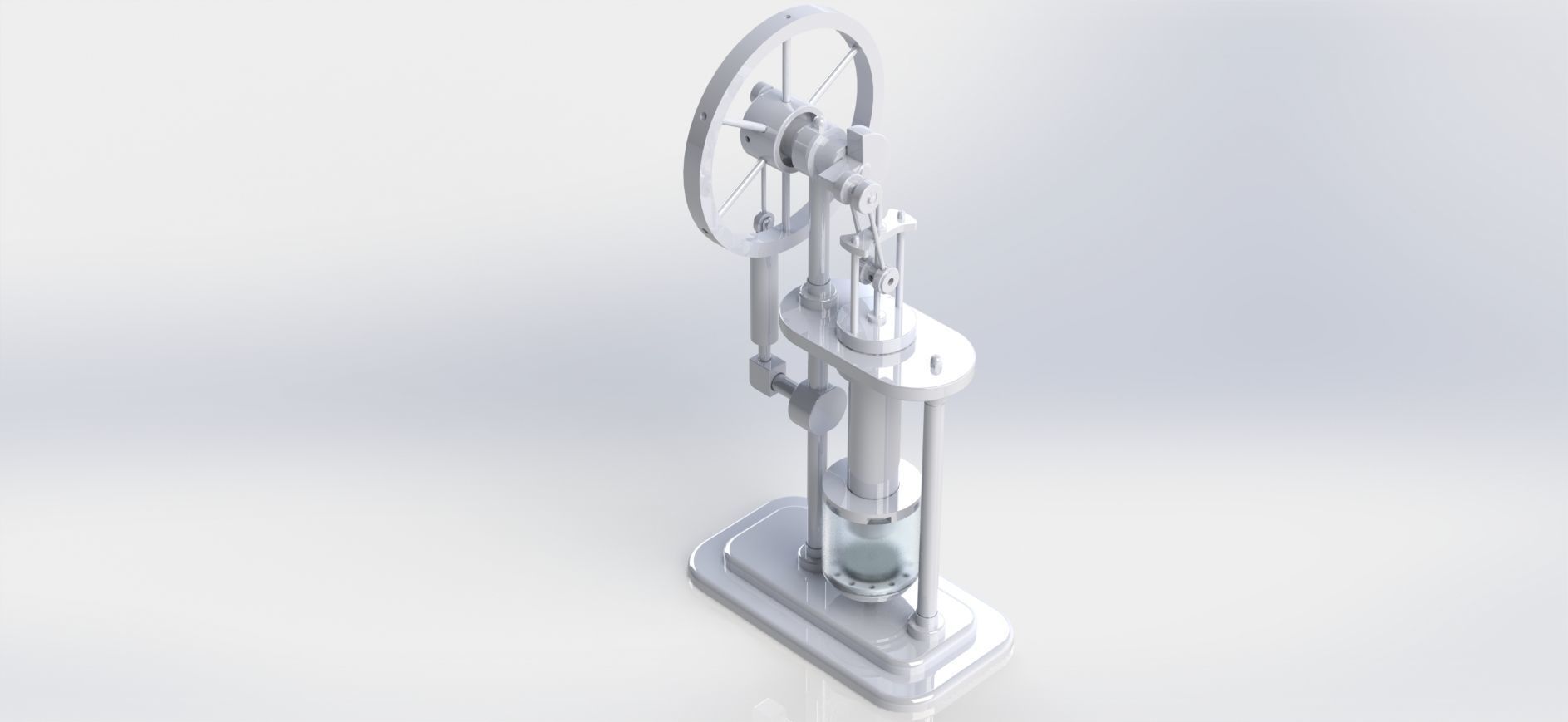
stirling hot air engine 3D model
stirling hot air engine solidwork part modelling and assembly solidwork motion study solidwork exploded view #letsmakeitcad #SolidWorks
A Stirling engine, also known as a Stirling hot air engine, is a type of heat engine that operates on the principle of cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gases at different temperatures. It was invented in 1816 by Scottish engineer Robert Stirling. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines that rely on combustion reactions, Stirling engines operate on a closed-cycle process using a working fluid, usually air or helium, which undergoes repeated heating and cooling.
Working Principle:
Compression: The working fluid (air or gas) is initially compressed in a cold chamber by a piston. This compresses the fluid and increases its pressure, causing its temperature to rise. Heating: The high-pressure, high-temperature working fluid is then transferred to a hot chamber where it is exposed to an external heat source. This heat causes the fluid to expand, pushing the piston outwards and doing mechanical work. Expansion: As the working fluid expands, its pressure decreases, and its temperature drops. Cooling: The expanded, lower-temperature fluid is moved to a cold chamber where it is exposed to a cooling medium, often air or water. This causes the fluid to contract and reduces its pressure. Return to Compression: The fluid is then returned to the initial cold chamber, and the cycle starts anew. Advantages:
Efficiency: Stirling engines can be highly efficient and have the potential for high theoretical efficiency levels due to their closed-cycle process and continuous heat exchange. Quiet Operation: Stirling engines operate silently compared to internal combustion engines because they lack combustion-related noise. Low Emissions: Since they operate without combustion, Stirling engines produce very low emissions. Disadvantages:
Complexity: Stirling engines can be complex to design and build due to their heat exchangers and precise thermal management requirements. Low Power-to-Weight Ratio: Stirling engines tend to have a lower power-to-weight ratio compared to internal combustion engines, limiting their use in certain applications. Slow Start-Up: Stirling engines can take a while to reach their optimal operating temperature, which might not be suitable for some applications. Applications:
Power Generation: Stirling engines can generate electricity, particularly in situations where fuel efficiency and low emissions are important. Heat Pumps: Stirling engines can be used as heat pumps or refrigerators when operated in reverse, transferring heat from a colder environment to a hotter one. Solar Power: They can be used in solar power systems to convert heat from concentrated sunlight into mechanical energy. Spacecraft: Stirling engines have been considered for use in spacecraft where waste heat from onboard systems can be utilized for power generation. Stirling engines are fascinating devices that have seen renewed interest in recent years due to their potential as efficient and environmentally friendly energy converters. However, their practical use often depends on specific applications, cost considerations, and engineering challenges.